Compliance
Full legal ESIGN, UETA, and eIDAS Compliance.
Learn what these acronyms mean, why they matter, and how Legal Signing helps you be fully compliant.
What is ESIGN?
The Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN), known as the E-Sign Act of 2000, allows electronic signatures to be legally binding where normally such a signature must be provided in writing. This ensures validity and compliance of any statute, regulation or rule of law.
What is UETA?
The Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) of 1999 ensures that electronic records and signatures are the legal equivalent of handwritten signatures on paper, making electronic commerce and transactions convenient.
Although very similar, the main difference between ESIGN and UETA is: States can adopt the UETA as they see fit, while ESIGN is federal legislation.
Together, these two electronic signature acts in the United States make e-signatures valid and legal on any forms, contracts or government documents for transactions that affect interstate or foreign commerce. They are important because they protect and legally enforce digital signatures on your contracts. Failure to comply may be treated as a withdrawal of consent and a technical violation of law.
What is eIDAS?
eIDAS stands for “electronic identification, authentication, and trust services.” Similar to ESIGN in the United States, eIDAS is a regulation established in the European Union (EU) that governs electronic signatures and transactions in the EU market. It was recently adopted in the UK as well.
One type of electronic signature that eIDAS recognizes is the Simple electronic signature. It’s a typical e-signature that does not require ID verification. Examples could be typing a name in a signature field of a form, using a scanned written signature, or writing your name under an email. These examples cannot be denied legal admissibility simply by virtue of being in electronic form.
Legally binding and fully compliant eSignatures.
Here’s how Legal Signing fulfills the four major requirements for an electronic signature to be recognized as valid under U.S. and EU law.
Requirement #1
Consent to Do Business Electronically
Each Signer is required to complete a consent field that verifies they consent to doing business electronically. We also provide a Consumer Disclosure that can be placed in your Terms of Service.
Requirement #2
Association of Signature with the Record
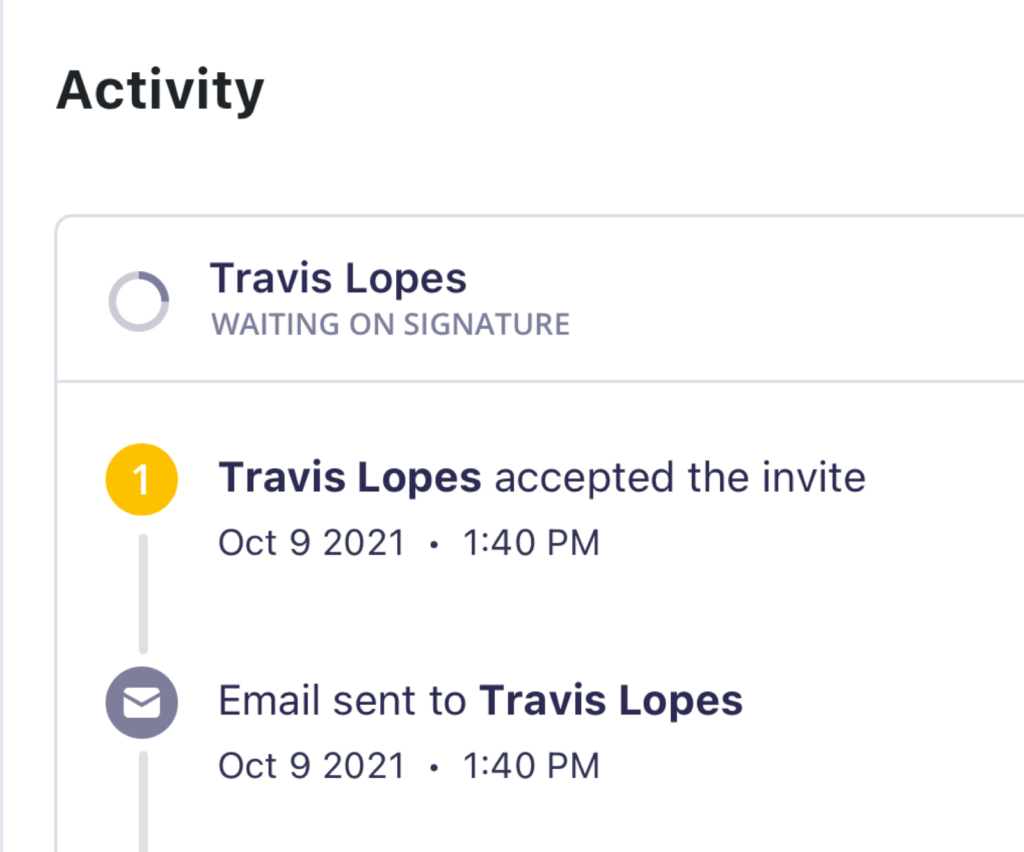
The activity of each Signer (notification of the need to sign, when they view the form, and their signing of the document) is tracked and associated with both their email address and IP address. This also fits the definition of a Simple electronic signature as defined by eIDAS.
Requirement #3
Record Retention
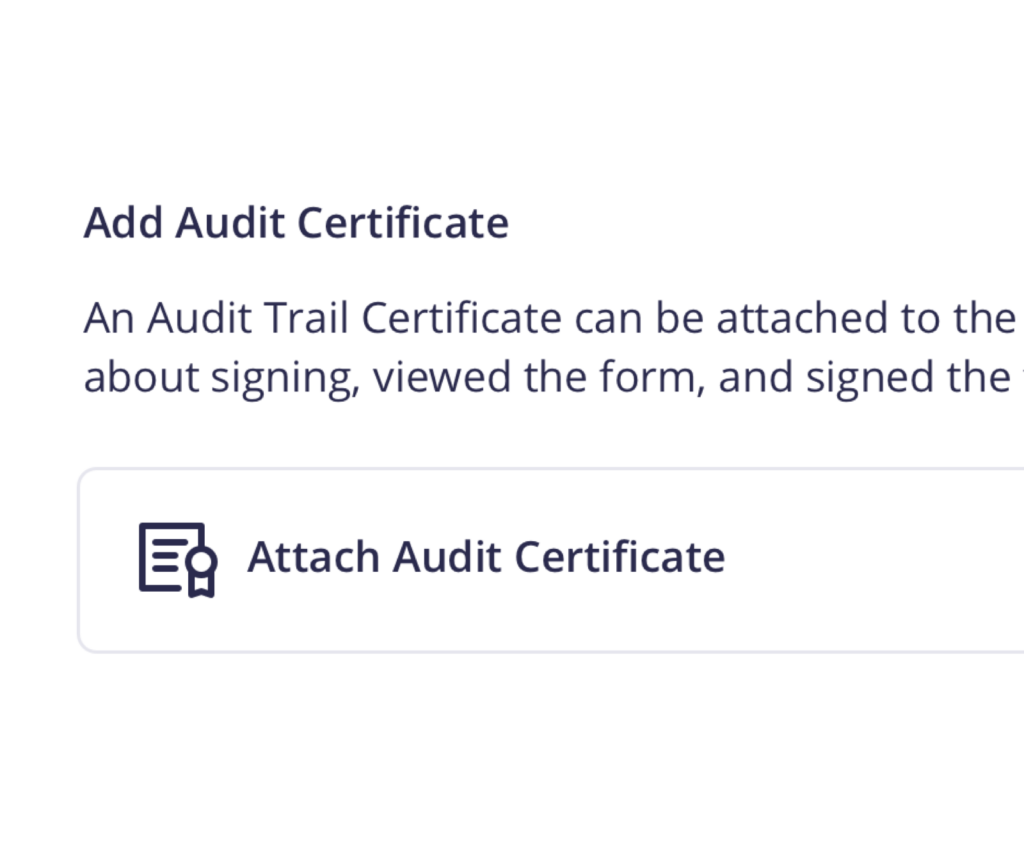
In addition to tracking the actions of each Signer, a certificate can be generated with the document that lists the activity of each Signer and gives both parties access and the ability to save the signed document.
Requirement #4
Intent to Sign
This requires the site owner to make it clear when creating the form that the user has intent to sign. Legal Signing will word the default consent field checkbox label to cover the Intent to Sign. Additionally, all signers will sign or verify their signature through unique links sent to their email. This identity verification system adds an extra layer of protection.
Note: If the user changes the checkbox label, we can’t guarantee that it is still compliant.
Ready? Get started.
Begin collecting legally binding eSignatures today.
